| [1] Chung SW, Kim SH, Tae SK, et al. Is the supraspinatus muscle atrophy truly irreversible after surgical repair of rotator cuff tears? Clin Orthop Surg. 2013;5:55-65. [2] Haviv B, Dolev E, Haber M, et al. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair:clinical outcome of 607 patients. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010; 18(12):1707-1711.[3] Baums MH, Kostuj T, Klinger HM, et al. Rotator cuff repair: single vs double-row. Clinical and biomechanical results. Orthopade. 2016;45(2): 118-124.[4] Deniz G, Kose O, Tugay A, et al. Fatty degeneration and atrophy of the rotator cuff muscles after arthroscopic repair: does it improve, halt or deteriorate? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134:985-990.[5] Fuchs B, Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, et al. Fatty degeneration of the muscles of the rotator cuff: assessment by computed tomography versus magnetic resonance imaging. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1999;8:599- 605.[6] Gerber C, Meyer DC, Frey E, et al. Neer Award 2007: reversion of structural muscle changes caused by chronic rotator cuff tears using continuous musculotendinous traction. An experimental study in sheep. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18:163-171. [7] Gerber C, Schneeberger AG, Hoppeler H, Meyer DC. Correlation of atrophy and fatty infiltration on strength and integrity of rotator cuff repairs: a study in thirteen patients. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16: 691-696. [8] Gladstone JN, Bishop JY, Lo IK, et al. Fatty infiltration and atrophy of the rotator cuff do not improve after rotator cuff repair and correlate with poor functional outcome. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35:719-728. [9] Goutallier D, Postel JM, Bernageau J, et al. Fatty muscle degeneration in cuff ruptures. Pre- and postoperative evaluation by CT scan. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;(304):78-83.[10] Goutallier D, Postel JM, Gleyze P, et al. Influence of cuff muscle fatty degeneration on anatomic and functional outcomes after simple suture of full-thickness tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12:550-554. [11] Harryman DT, Mack LA, Wang KY, Jackins SE, Richardson ML, Matsen FA. Repairs of the rotator cuff. Correlation of functional results with integrity of the cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73:982-989.[12] Hislop HJ. Daniels and Worthingham’s muscle testing: techniques of manual examination. Philadelphia: Saunders, USA. 1995.[13] Jo CH, Shin JS. Changes in appearance of fatty infiltration and muscle atrophy of rotator cuff muscles on magnetic resonance imaging after rotator cuff repair: establishing new time-zero traits. Arthroscopy. 2013;29:449-458. [14] Kim SJ, Kim SH, Lee SK, et al. Arthroscopic repair of massive contracted rotator cuff tears: aggressive release with anterior and posterior interval slides do not improve cuff healing and integrity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:1482-1488. [15] Kim SJ, Lee IS, Kim SH, et al. Arthroscopic repair of concomitant type II SLAP lesions in large to massive rotator cuff tears: comparison with biceps tenotomy. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:2786-2793. [16] Kundel HL, Polansky M. Measurement of observer agreement. Radiology. 2003;228:303-308.[17] Sarah E. Rehabilitation guidelines after rotator cuff repair. Tech Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;15(1):8-12.[18] Laron D, Samagh SP, Liu X, et al. Muscle degeneration in rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21:164-174. [19] Liem D, Lichtenberg S, Magosch P, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of arthroscopic supraspinatus tendon repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:1770-1776.[20] Melis B, Wall B, Walch G. Natural history of infraspinatus fatty infiltration in rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19:757-763. [21] Shen PH, Lien SB, Shen HC, et al. Long-term functional outcomes after repair of rotator cuff tears correlated with atrophy of the supraspinatus muscles on magnetic resonance images. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008; 17:1S-7S. [22] Tan M, Lam PH, Le BT, et al. Trauma versus no trauma: an analysis of the effect of tear mechanism on tendon healing in 1300 consecutive patients after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016;25:12-21. [23] Thomazeau H, Rolland Y, Lucas C, et al. Atrophy of the supraspinatus belly. Assessment by MRI in 55 patients with rotator cuff pathology. Acta Orthop Scand. 1996;67:264-268.[24] Visonà E, Paladini P, Merolla G, et al. Strength recovery after arthroscopic anterosuperior cuff repair: analysis of a consecutive series. Musculoskelet Surg. 2015;99(Suppl 1):37-42. [25] Yamaguchi H, Suenaga N, Oizumi N, et al. Will preoperative atrophy and fatty degeneration of the shoulder muscles improve after rotator cuff repair in patients with massive rotator cuff tears? Adv Orthop. 2012 ; 2012:195876. [26] De Orio JK, Cofield RH. Results of a second attempt at surgical repair of a failed initial rotator-cuff repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(4):563-567.[27] Schaefer O, Winterer J, Lohrmann C, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging for supraspinatus muscle atrophy after cuff repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(403):93-99.[28] Thomazeau H, Boukobza E, Morcet N, et al. Prediction of rotator cuff repair results by magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;(344):275-283.[29] Barry JJ, Lansdown DA, Cheung S, et al. The relationship between tear severity, fatty infiltration, and muscle atrophy in the supraspinatus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(1):18-25.[30] Fabbri M, Ciompi A, Lanzetti RM, et al. Muscle atrophy and fatty infiltration in rotator cuff tears: Can surgery stop muscular degenerative changes? J Orthop Sci. 2016;21(5):614-618.[31] 刘宇,顾三军,徐耀增.巨大肩袖损伤的诊治现状与进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(9):823-828.[32] 孙程,卢翔,马金忠.巨大肩袖撕裂治疗现状[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2017, 25(20):1876-1880.[33] 任江涛,徐丛.关节镜下缝线桥技术修复肩袖撕裂的缝合及固定方式研究进展[J].中华骨科,2016,36(7):443-448. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
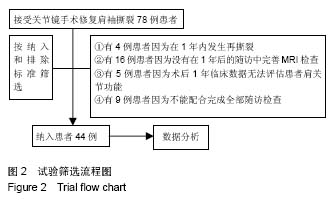
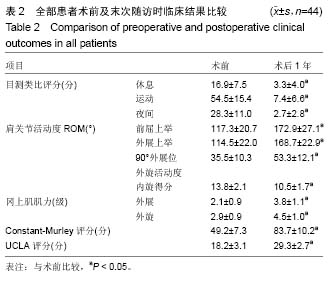
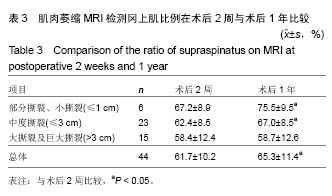
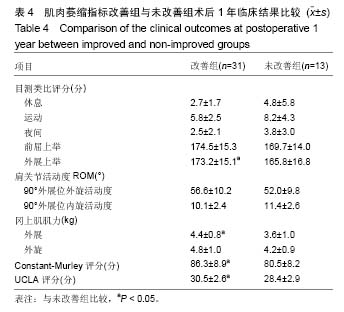
.jpg)
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
肩袖:又叫旋转袖,是包绕在肱骨头周围的一组肌腱复合体,这些肌腱的运动导致肩关节旋内,旋外和上举活动。#br#
冈上肌:该肌受肩胛上神经支配,其作用是上臂外展时的起动。冈上肌被斜方肌和三角肌覆盖,其肌腱与冈下肌、肩胛下肌及小圆肌共同组成肩袖。#br#
#br#
#br#
文题释义:#br#
肩袖:又叫旋转袖,是包绕在肱骨头周围的一组肌腱复合体,这些肌腱的运动导致肩关节旋内,旋外和上举活动。#br#
冈上肌:该肌受肩胛上神经支配,其作用是上臂外展时的起动。冈上肌被斜方肌和三角肌覆盖,其肌腱与冈下肌、肩胛下肌及小圆肌共同组成肩袖。#br#
#br#